- Details
- Written by user
- Category: Uncategorised
- Hits: 1096
Уважаемые жители и гости города Астаны!
Наши лабораторные услуги предназначены для удовлетворения Ваших потребностей:
Лабораторные анализы выполняет высококвалифицированный персонал (100% категорийность врачебного персонала и 100% категорийность среднего персонала) в соответствии с установленными стандартами
Лаборатория имеет 100% оснащение оборудованием (автоматическое и полуавтоматическое)для проведения исследований
В лаборатории установлена лабораторная информационная система, позволяющая работать в едином информационном поле с медицинскими организациями.
Качество лабораторных исследований обеспечивается проведением внутрилаборатоного кантроля качества и участием лаборатории во внешней оценке качества
В своей деятельности лаборатория стремится выполнять требования международного стандарта ISO 15 189.
Результаты международного оценочного визита 2013 год
2017
Результаты международного оценочного визита 2014 год
2014
sertifikat 00000000
Лабораторная диагностика инфекций, проводится на тест системах Российских и зарубежных производителей
Лабораторная диагностика ВИЧ проводится на тест-системах IV поколения
04.150000000000
SAM 154900000
- Details
- Written by Admin
- Category: Uncategorised
- Hits: 20208
Изображение 001
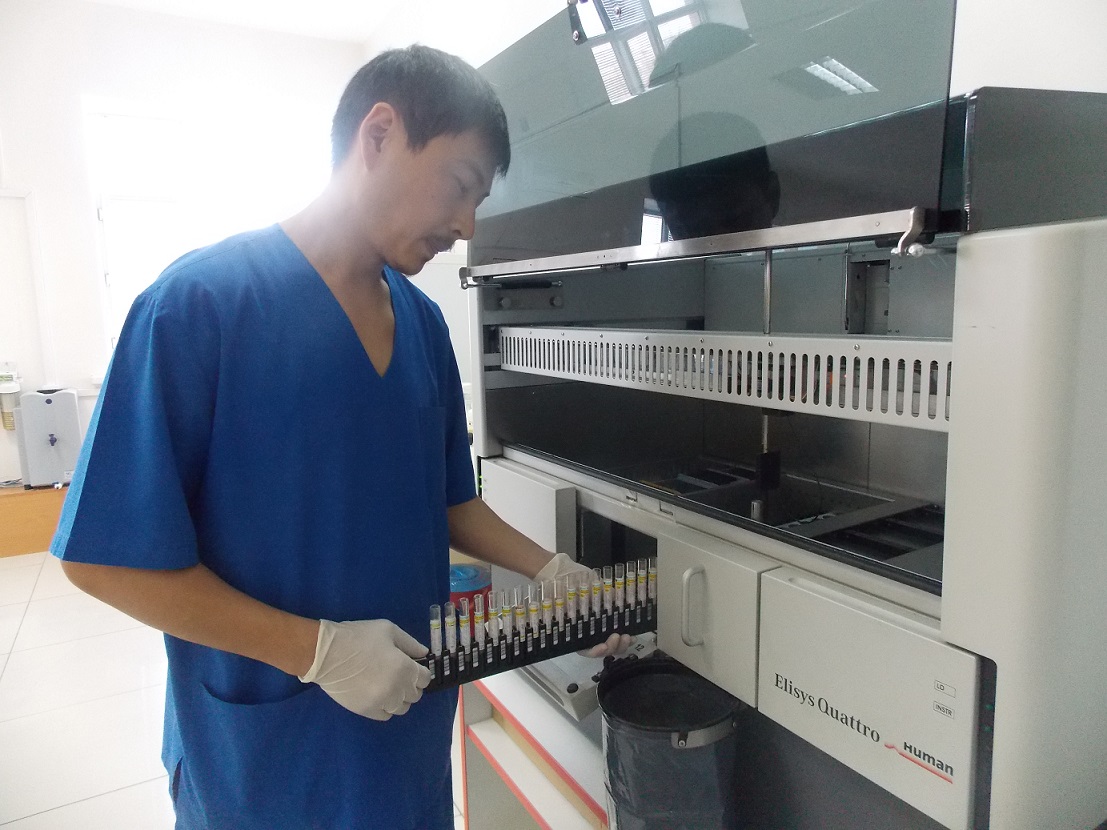
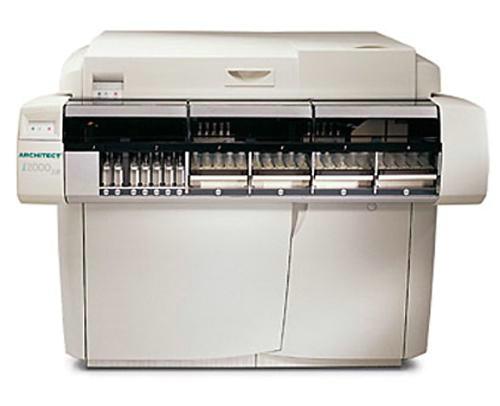
В лаборатории для апробации установлен новый прибор- Иммунохимический анализатор Architect i2000 фирмы ABBOTT- мирового лидера по производству лабораторного оборудования
Характеристики прибора:
Иммунохимический анализатор ABBOTT Architect i2000 - анализатор с хемилюминисцентной технологией Chemiflex, обеспечивает превосходное качество анализов с минимальными затратами на их проведение и максимальной производительностью. Обеспечивает возможность проведения анализов по ВИЧ-диагностике, вирусных гепатитов и других инфекций.
Имеет несколько режимов работы:
- немедленный доступ: загрузка приоритетных тестов без прерывания работы анализатора;
- последовательный доступ: загрузка до 125 образцов на модуль;
- произвольный доступ: анализ образцов производится в любом заданном порядке.
- время получения первого результата - 28 мин, каждый последующий - через 18 сек.
- производительность до 200 тестов/час на модуль.
Тест системы IV поколения, которые используются для диагностики ВИЧ инфекции
Сертификаты участия в Внешней оценке качества (ВОК)
по программам ВИЧ/Гепатиты, клиническая химия и гематология
- Details
- Written by Admin
- Category: Uncategorised
- Hits: 1302
Public service «Anonymous and Voluntary mandatory confidential medical examination for the presence of HIV infection» are made by the medical organizations that provide primary health care, Centre for prevention and control of AIDS of the city of Astana (hereinafter «service provide»). The deadline for the provision of public services:
1) from the moment of ologopolistic package of documents to the provider - negative result of the examination shall be 3 (three) working days; a positive result of the examination is 20 (twenty) working days;
2) the maximum waiting time for delivery of documents - not more than 30 (thirty) minutes;
3) the maximum service time of plugouts - not more than 60 (sixty) minutes.
The form of the provision of public services is paper.
The result of rendering the state service – help certificate confirming the negative results of public services.
Help certificate is valid for 3 (three) months from the date of its issuance.
In case of negative result of the survey is the result of rendering the state service is issued to plugability personally on hand.
Upon receipt of the primary positive result the service provider provided blood samples for re-testing for antibodies to HIV.
In the case of a positive final results the result of rendering the state service shall be issued in the form of a written notification to plugability personally on hand.
The results of rendering the state service of minors and incapacitated plugability are issued by the service provider to their parents or other legal representatives.
Public service is provided to plugability free physical persons (citizens of the Republic of Kazakhstan and oralmans), requiring payment to individuals (foreigners and persons without citizenship).
Admission takes place in the order queue, scheduling and expedited service are not provided. The list of documents required for the provision of public services by contacting plug outs: when receiving services mandatory medical examination for the presence of HIV - identity document (for persons under sixteen years of age - birth certificate).
When receiving the service anonymous medical examination for HIV infection no documents are required, the user is assigned an individual code.
- Details
- Written by Admin
- Category: Uncategorised
- Hits: 1443
The main measure to prevent the spread of HIV is teaching people skills are less dangerous in terms of HIV transmission behavior. Some groups, distinguished by certain peculiarities of behavior or lifestyle, may be exposed to relatively higher risk of HIV infection. To protect oneself from HIV infection can knowing the properties of the virus, its transmission and prevention.
The little virus is resistant to the active factors of the external environment, for example at a temperature of 56°C inactivated within half an hour, at 100°C for 1-2 minutes. At the same time in a frozen state HIV may persist for several years.
In dried blood on needles and syringes, as well as in solutions of drugs can retain its activity for up to 3 weeks or more (at room temperature), and in some cases, probably up to a month, which is one of the most important factors contributing to its spread among injecting drug users.
In the presence of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), the risk of HIV transmission during sexual intercourse increases by 2-5 times.
The presence of sexually transmitted infections, accompanied by the emergence of open sores (e.g., herpes), is especially dangerous.
If there is no contact with blood, semen, vaginal secretion, the possibility of HIV infection is excluded.
There are several ways of HIV transmission:
- unprotected (without a condom) penetrative sexual contact;
- joint or reuse syringes, needles and other injecting equipment, the use of non-sterile equipment for tattoos and piercing, use of other people's shaving set, toothbrush holder with remnants of blood;
- during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding from an HIV-infected mother to child.
HIV is not transmitted through:
- insect bites;
- the hugs, shaking hands;
- sharing of bath, bath, pool, toilet;
- sharing linens, kitchenware and other household items;
- sneezing and coughing;
- friendly kisses;
- safe sex.
Prevention of sexual transmission of HIV
Condoms guaranteed quality are the only products currently available to protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV.
Consistent condom use during sexual contacts is currently the most reliable method of preventing infection how to homosexual and heterosexual.
During anal sex acts in which a condom is subjected to more mechanical impact, increasing the risk of rupture, it is recommended to use a more durable (often specially marked) condoms and lubricants (lubricants).
To reduce the risk of HIV infection by parenteral (through the blood):
- using each drug new, previously no one used syringe and needle, if it is impossible to use only their "personal" syringe and needle, which is no longer used;
- using the introduction of the solution which was prepared in the conditions excluding contact with blood of another person;
- a boiling solution of the drug directly to the introduction, not washing your individual syringe in one capacity syringes which were used by others.
Prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs
Prevention of infection by sexually transmitted infections, and other inflammatory diseases of sexual sphere, leads to a decrease in the number of inflammatory processes in the genital organs, increasing the risk of HIV transmission.
Prevention of STI is carried out by the methods of education that has the same orientation as the HIV prevention: reducing the number of partners and condom use. As control measures, aimed at the source of infection for many infections, genital effectively etiotropic treatment, leading to the rehabilitation of the infected person.
Systematic treatment of infectious lesions of the genitals, providing the frequency and intensity of inflammatory processes also potentially reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
All about HIV/AIDS
Despite comprehensive information about HIV transmission routes and prevention methods, unfortunately, the HIV epidemic is not reduced. To understand the principles of HIV prevention is easy. This virus does not live outside the body fluids of a person not transmitted through casual contact, and each person has the opportunity to protect themselves from HIV and to help their loved ones.
Thus, HIV - human immunodeficiency virus. When injected into the human body, HIV destroys the immune system, which protects us from disease and infection. The human immunodeficiency virus belongs to the family of retroviruses (Retroviridae), the genus of lentiviruses (Lentivirus). Name Lentivirus comes from the Latin word lente - slow. This name reflects one of the characteristics of the viruses of this group, namely the slow and uneven rate of development of infectious process in the host. Lentiviruses are characterized by a long incubation period.
The virus is found in all bodily fluids and tissues of the body. According to the degree of concentration of the virus in the body: blood, lymph, semen, vaginal secretions. In the rest of the body fluids of the contents of the virus is not sufficient for infection (saliva, tears, sweat, urine, feces, and other).
The human immunodeficiency virus was discovered in 1983 in the study of the etiology of AIDS. The first official scientific reports of AIDS were two articles about unusual cases, the development of Pneumocystis pneumonia and Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men, published in 1981. In July 1982 for the first time to denote a new disease, the term AIDS was proposed. In September of the same year on the basis of a number of opportunistic infections diagnosed in homosexual men, drug users, patients with hemophilia A, AIDS was first given full definition as a disease. Several works were published in the period from 1981 to 1984, linking the risk of AIDS from anal sex or the influence of drugs. Simultaneously been working on a hypothesis about the possible infectious nature of AIDS. In 1983, HIV was independently discovered in two laboratories: the Institute Pasteur in France under the direction of Luc Montagnier and at the National cancer Institute in the United States under the leadership of Robert Gallo.
According to research published may 20, 1983 was the first to allocate a new retrovirus. Researchers have assumed that their viruses can cause AIDS.
In 1986 it was discovered that the virus, discovered in 1983 by French and American researchers were genetically identical. Original title of the viruses were abolished and was proposed one common name - HIV.
In 2008, Luc Montagnier and Francoise Barre-Sinoussi were awarded by the Nobel prize in physiology and medicine «for their discovery of human immunodeficiency virus».
HIV infects primarily cells of the immune system (CD4+ T-lymphocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells), as well as some other types of cells. Extending into the cells of the specified types, the virus begins to multiply. This, ultimately, leads to the destruction and death of the infected cells. The presence of HIV over time causes a disturbance of the immune system due to selective destruction of them immunocompetent cells and suppress their subpopulations. Released viruses are introduced into the new, and the cycle repeats. Gradually the number of CD4+ lymphocytes is reduced so that the body can no longer withstand the causative agents of opportunistic infections, which are not dangerous or not dangerous for healthy people with normally functioning immune system.
AIDS - acquired immune deficiency syndrome, last, end-stage disease, the result of the destruction of a significant part of the human immune system. HIV can weaken the immune system to a specific state, when the body starts to develop so-called opportunistic diseases. The diagnosis AIDS is usually made some years later after HIV infection, when at the person one or several very serious diseases to which leads the progressing weakening of immune system owing to corrupting of CD4+ of lymphocytes develop. The current antiretroviral therapy reduces the activity of the virus and reduce the harm it causes to the immune system, preventing, thus, the development and transition of HIV into AIDS.